In the realm of agile project management, the term “story points” holds significant importance. It’s a metric used by agile teams to estimate the relative effort required to complete a user story or task during a sprint. Understanding story points is crucial for effective sprint planning, resource allocation, and progress tracking. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the concept of story points, provide examples to illustrate their use, explore why agile teams rely on them, and detail how to calculate them accurately. By the end of this journey, you’ll have a clear understanding of story points and their role in driving successful agile development cycles. So, let’s embark on this enlightening exploration of story points in the agile landscape.
Contents
What Are Story Points?
In the dynamic world of agile project management, story points serve as a unit of measure representing the effort required to complete a particular user story or task. Unlike traditional time-based estimations, such as hours or days, story points focus on the relative complexity and effort involved in delivering a piece of work. This relative scale allows agile teams to assess the size and complexity of user stories to one another, rather than fixating on absolute timeframes.

Story points provide a more flexible and accurate way to estimate work, accommodating the inherent uncertainties and complexities of software development projects. By assigning story points to user stories, teams can prioritize tasks effectively, allocate resources efficiently, and plan sprints with greater confidence. Now, let’s delve deeper into how story points are applied in agile development.
→ Related content: Streamlining Agile Estimating with Story Points
Why Do Agile Teams Use Story Points?
Agile teams opt for story points over traditional time-based estimations for several compelling reasons.
Facilitates Better Sprint Planning
Story points enable agile teams to plan sprints more effectively by providing a reliable measure of the effort required for each user story. This approach helps in balancing workloads and setting realistic sprint goals, ensuring that teams neither overcommit nor underutilize their capacity. Consequently, this leads to successful sprint completions and maintains high team morale.
Promotes Team Collaboration and Consensus
The process of assigning story points requires input from all team members, making it a collaborative effort that builds consensus. This method not only enhances the accuracy of estimates but also ensures a shared understanding of project tasks. Such collaboration fosters team cohesion and aligns member expectations, crucial for agile environments where flexibility and rapid adjustments are common.

Enables More Accurate Forecasting and Tracking
Story points provide a consistent unit of measure for team productivity, unaffected by individual pace differences or unexpected challenges. By tracking the completion of them over sprints, teams can refine their future planning and estimates, leading to improved predictability and efficiency in project workflows.
Supports Flexibility and Continuous Improvement
The use of story points in agile projects supports the principle of continuous improvement by allowing for the re-evaluation and adjustment of task complexity as the team’s performance evolves. This flexibility is key to agile methodology, enabling teams to adapt their processes and improve efficiency over time, thus delivering greater value to stakeholders.

How Do You Calculate Story Points?
Calculating story points is a crucial aspect of agile project management, facilitating effective sprint planning and workload estimation. This process is inherently collaborative, involving all team members to ensure a comprehensive understanding and assessment of each task or user story’s complexity.
The Role of Planning Poker in Agile Estimation
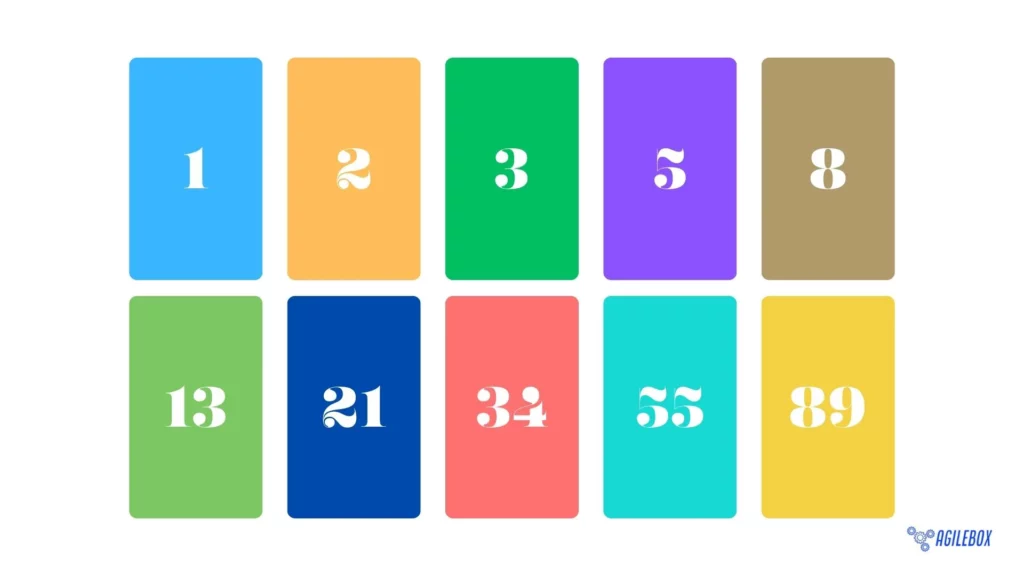
A popular technique employed by agile teams for this purpose is “planning poker,” a consensus-based estimation method designed to assign story point values to user stories. In planning poker, team members are equipped with a set of cards, each denoting a different story point value. These values often follow the Fibonacci sequence, including numbers such as 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, etc., to represent the relative effort and complexity involved in completing a user story.
→ Related content: Planning Poker Explanation | Beginner’s Guide to Planning Poker by AgileBox
The Estimation Process Detailed
The estimation process begins with the product owner or a facilitator introducing a user story to the team. Following this introduction, each team member selects a card from their deck that they believe best represents the story’s complexity and the effort required to complete it. This selection is made individually, ensuring that each estimate is based on personal insight and understanding.
After all team members have made their selections, they reveal their chosen cards simultaneously. This method prevents anyone’s estimate from influencing others, promoting an unbiased and fair estimation process.
Reaching Consensus Through Discussion
Discrepancies in the initial estimates are not uncommon and are addressed through open discussion among the team members. These discussions aim to clarify any misunderstandings, highlight different perspectives, and address uncertainties that may have influenced the varied estimates. The process continues until the team reaches a consensus on a final story point value for the user story.

The Benefits of Collaborative Estimation
This collaborative approach to estimation not only fosters transparency and alignment within the team but also leverages the collective experience and wisdom of all team members. It allows for more accurate and reliable estimates by incorporating diverse perspectives and insights. Through this method, agile teams can make informed decisions, effectively prioritize their workload, and deliver maximum value to their stakeholders. Now, let’s explore how Agilebox’s Planning Poker tool enhances this collaborative process for agile teams.
Story Points Best Practice
Story points are a way to estimate the effort required to complete user stories or tasks. Here are some valuable guidelines:
Collaborate with the Product Owner
The product owner prioritizes the backlog, but they might not fully understand the implementation details. Engage in discussions to break down work items and estimate their effort. This helps the product owner gain insights into the level of effort for each task, which informs their relative priority.
Involve the Entire Team
Story point estimation is a team effort. Gather input from developers, designers, testers, and other team members. Each perspective contributes to a holistic understanding of the work. For instance, design changes require input not only from the design team but also from development and QA.

Avoid Averaging Story Points
Don’t average story points across tasks. Each task has unique characteristics, risks, complexities, and uncertainties. Story points capture the whole picture, so treat each item individually.
Remember: It’s an Estimate, Not a Blood Oath
Agile story points estimation is just that—an estimate. It’s not a binding commitment. There’s no need to work weekends to compensate for underestimating a piece of work. Keep it flexible and adapt as needed.
→ Related content: What is a User Story and why is it important?
Playing Planning Poker by AgileBox Brings You the Best Teamwork
Tools like AgileBox’s Planning Poker offer invaluable support to teams aiming for seamless collaboration and accurate estimations. AgileBox provides a user-friendly platform that streamlines the planning poker process, facilitating efficient communication and decision-making among team members.
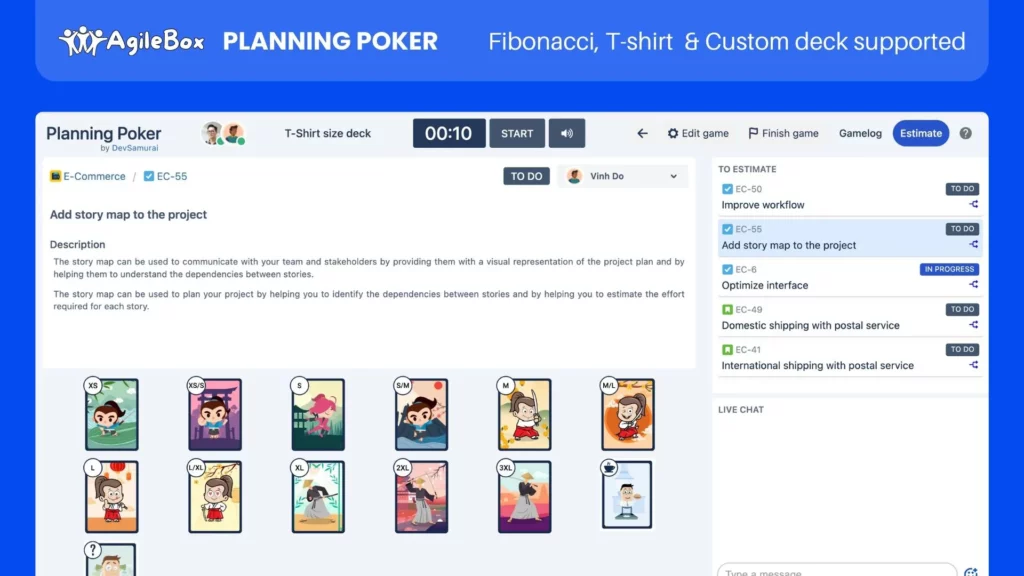
With Agilebox, teams can easily create estimation sessions, invite participants, and conduct estimations in real time, regardless of their physical location. The platform offers customizable card decks, allowing teams to tailor the estimation scale to their specific needs and preferences.
→ Try out AgileBox – Planning Poker, Agile Retrospectives, Daily Standup for Jira
Additionally, Agilebox features built-in timers and facilitation tools to keep estimation sessions focused and productive. By leveraging Agilebox’s Planning Poker, agile teams can harness the power of collective intelligence, foster collaboration, and arrive at consensus-based estimations that drive successful project outcomes. Now, let’s conclude our exploration of story points and agile estimation.
Conclusion
Story points serve as a fundamental concept in agile development, enabling teams to estimate and prioritize work effectively. By focusing on relative complexity and effort rather than fixed timeframes, agile teams gain flexibility and accuracy in their estimations. Through techniques like planning poker and tools like Agilebox’s Planning Poker, teams can foster collaboration, transparency, and consensus-building during the estimation process. This collaborative approach enhances team cohesion, facilitates informed decision-making, and ultimately contributes to the successful delivery of value to stakeholders. As you continue your agile journey, remember to embrace story points as a valuable tool for navigating complexity, adapting to change, and driving continuous improvement in your projects. Harness the power of story points and agile estimation to propel your team towards greater success and satisfaction in your agile endeavors.













