Contents
I. Introduction
Project management is the process of planning, organizing, executing, and controlling a project to achieve specific goals and objectives. Project management is essential for delivering successful outcomes in any industry, as it helps align the project scope, schedule, budget, quality, and risks with the stakeholders’ expectations.
There are two primary approaches to project management: Agile and Traditional.
- Agile project management is an iterative and adaptive approach focused on delivering value to the customer in short cycles called sprints. It embraces change and feedback and empowers the project team to self-organize and make decisions.
- Traditional project management is a linear and predictive approach that follows a predefined sequence of phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure. It relies on detailed upfront planning and documentation and aims to minimize changes and deviations from the plan.
II. Understanding Traditional Project Management
Definition
Traditional project management is a linear and sequential approach to managing projects. It follows a structured process that involves detailed planning, strict control, and sequential execution of project activities. This approach assumes that project requirements can be fully defined at the beginning and that changes to requirements are minimized throughout the project lifecycle.
Key Characteristics
Key Characteristics of Traditional Project Management:
- Detailed Planning: Traditional project management emphasizes thorough planning before project execution begins. This involves defining the project scope, creating a detailed project plan, estimating resources and timelines, and identifying dependencies between tasks.
- Strict Control: This approach maintains strict control over project activities through monitoring and evaluation. Progress is tracked against the predetermined plan, and any deviations are analyzed and managed accordingly.
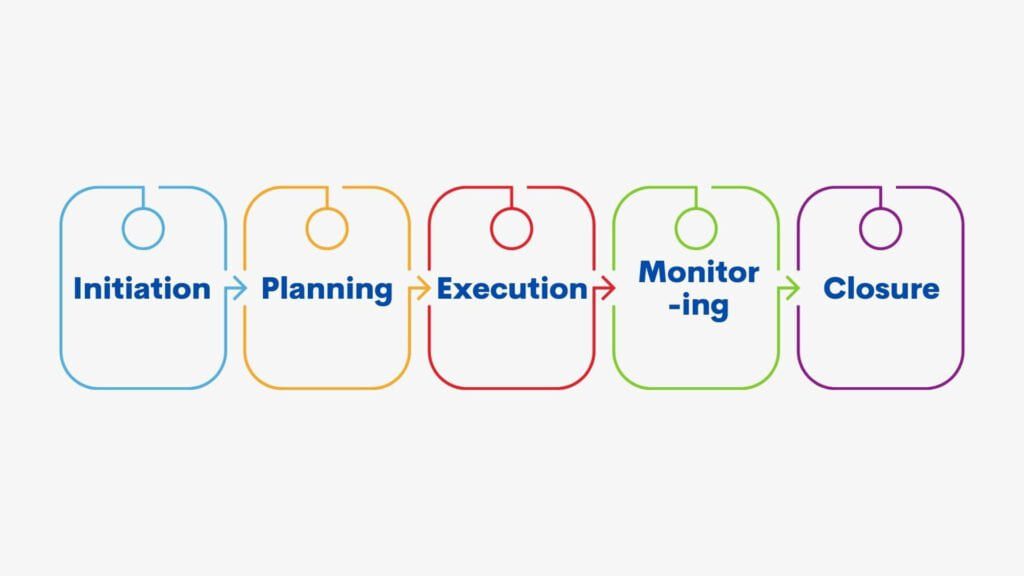
- Sequential Execution: Projects following the traditional approach typically progress in a linear, sequential manner. Each project phase (e.g., initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure) is completed before moving on to the next, with little room for overlap or iteration.
The Waterfall Model
The waterfall model is a representative example of traditional project management. It consists of sequential phases: requirements gathering, system design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase has clearly defined inputs, outputs, and milestones. The waterfall model follows a “one-way” flow, where progress moves linearly from one phase to the next, and it is challenging to revisit or make changes once a phase is completed.
While the traditional project management approach has been widely used and proven successful in specific contexts, it has limitations. The rigid nature of the approach can make it challenging to adapt to changing requirements or unforeseen issues. Additionally, the sequential execution may result in late identification of problems, as feedback and testing occur toward the end of the project lifecycle. These limitations have led to the adoption of Agile project management methodologies that prioritize flexibility, collaboration, and iterative development.
III. Introducing Agile Project Management
Definition
Agile project management is an iterative and flexible approach emphasizing adaptability, collaboration, and delivering value in small increments. It empowers cross-functional teams to work collaboratively, respond to change quickly, and continuously improve throughout the project lifecycle.
Agile project management’s iterative and incremental nature allows for frequent inspection, adaptation, and continuous improvement. The team divides projects into small iterations or sprints, where each iteration delivers a working product increment. They actively solicit feedback from stakeholders and end-users and incorporate it into subsequent iterations. This approach enables early value delivery and mitigates the risk of delivering a product that doesn’t meet expectations.
Core Principles
Core principles of Agile project management include:
- Customer Collaboration: Agile emphasizes close collaboration with customers, ensuring the delivered product meets their evolving needs.
- Responding to Change: Agile embraces change as a competitive advantage, encouraging teams to be flexible and responsive.
- Working Solutions: Agile prioritizes tangible deliverables over extensive documentation, promoting iterative development.
- Individuals and Interactions: Agile emphasizes collaboration, effective communication, and valuing team members’ skills and expertise.
Scrum & Kanban
Two popular Agile methodologies are:
Scrum: Scrum is an iterative and incremental Agile framework focusing on collaboration, transparency, and effective team communication. It follows a time-boxed approach, with work organized into fixed-length iterations called sprints. Scrum teams self-organize and work in cross-functional units to deliver incremental value.
Kanban: Kanban is an Agile framework that visualizes the workflow, promotes continuous flow, and limits work in progress (WIP). It provides a visual board where tasks move across different stages of completion, enabling teams to track progress and identify bottlenecks. Kanban emphasizes efficiency and encourages delivering small, frequent, and high-quality work.
Read more here: Kanban or Scrum, which one is for you?
IV. The Benefits of Agile Project Management
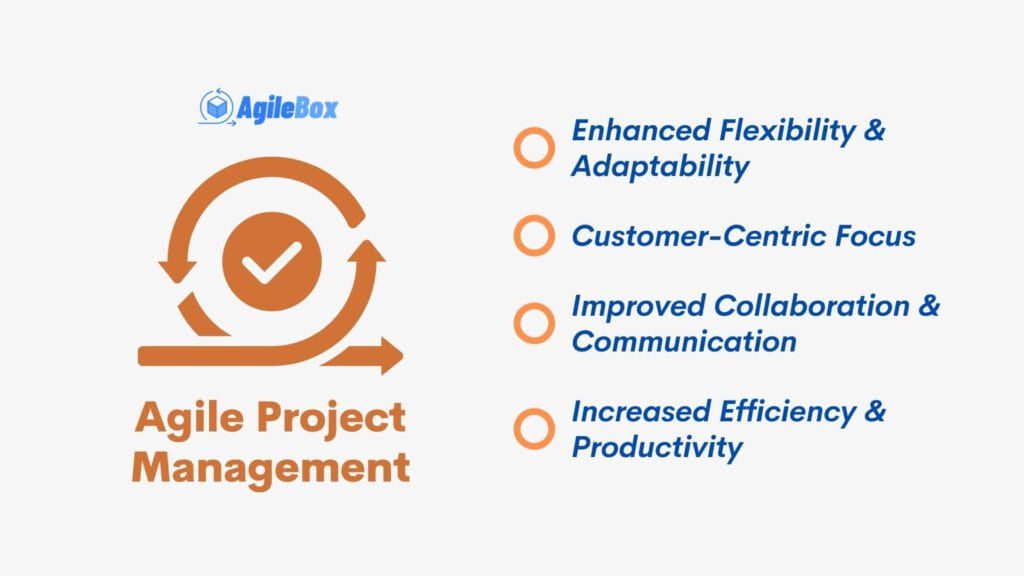
A. Enhanced Flexibility and Adaptability
Agile project management uses an iterative approach, breaking projects into small increments. This allows teams to respond to changes and customer feedback effectively. Each iteration delivers a working product increment, gathers insights, and incorporates adjustments. This ensures the final product meets evolving customer needs.
Embracing change in Agile project management offers several advantages. It enhances customer satisfaction through active involvement and incorporating feedback, prioritizes early value delivery for faster time-to-market, enables risk mitigation through adaptability, and fosters continuous improvement by seeking feedback and making iterative adjustments. This approach drives efficiency, productivity, and project success.
B. Customer-Centric Focus
Agile methodologies have a strong customer-centric focus. They prioritize frequent customer involvement, encouraging active participation in the project for feedback, requirement clarification, and validation. Agile also promotes continuous feedback loops, enabling customers to provide input, evaluate progress, and suggest changes. This iterative feedback process drives a continuous improvement cycle, ensuring a product is closely aligned with customer needs.
Agile’s customer-centric approach brings several benefits: enhanced customer satisfaction through involvement and meeting needs, early validation reducing risk, proactive risk management, increased flexibility in adapting to evolving needs, and refinement of project requirements based on customer feedback. This iterative approach ensures the final product aligns with customer expectations and the market landscape.
C. Improved Collaboration and Communication
Agile methodologies promote collaboration and communication through cross-functional teamwork and open channels. Agile teams leverage their members’ diverse skills and expertise, fostering a collaborative environment where knowledge and ideas are shared. Regular interactions, including daily stand-ups and team check-ins, facilitate open and transparent communication, ensuring alignment, progress updates, and timely issue resolution.
Promoting transparency and empowering team members in Agile project management brings advantages such as increased productivity, rapid issue resolution, continuous learning and improvement, and enhanced team morale and satisfaction.
D. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Agile utilizes an iterative approach, breaking projects into sprints that deliver working increments of the product. This iterative process allows for early and frequent showcases of tangible results. Additionally, Agile promotes continuous improvement as teams learn from feedback and optimize processes with each iteration.
Shorter feedback loops in Agile enable quick validation, reducing rework and ensuring the final product meets customer needs. Agile’s iterative approach and early issue identification minimize rework, saving time and resources. This faster time-to-market is achieved through incremental value delivery and the ability to respond promptly to market demands. Agile methodologies also increase productivity through transparency, collaboration, and team empowerment, optimizing processes and maximizing output.
V. Overcoming Traditional Project Management Challenges
A. Traditional Project Management Challenges
Traditional project management, often referred to as the Waterfall methodology, can present several key challenges.
- Scope Creep. One of the most common challenges is scope creep or the tendency for the project’s scope to expand beyond its original objectives. Since traditional project management often requires a detailed and rigid plan upfront, changes in requirements or objectives can result in increased costs, delays, and potential conflicts.
- Delayed Feedback. In traditional project management, feedback is typically gathered towards the end of the project, once a product or solution has been fully developed. At this stage, if there are significant issues identified, making changes can consume time and incur high costs.
- Limited Adaptability. Traditional project management struggles with adaptability due to its linear approach. Unforeseen changes such as new market developments, changes in technology, or resource shifts can be challenging to accommodate, often leading to delays or project failure.
B. How Agile Project Management Addresses These Challenges
Agile project management, with its emphasis on flexibility and continuous improvement, offers solutions to these challenges.
- Mitigating Scope Creep. Agile employs iterative development, where it breaks down the project into smaller, manageable units or “sprints.” This approach enables regular prioritization and review of features and requirements. If there are changes to the scope, the team incorporates them into the next sprint, helping to maintain project alignment and minimize the risk of uncontrolled expansion.
- Immediate and Continuous Feedback: Agile promotes active stakeholder involvement and frequent delivery of working software, allowing for continuous feedback throughout the project. Getting feedback early and often can identify and rectify issues quicker than in traditional project management. This results in products that better meet user needs and expectations.
- Enhanced Adaptability: The Agile methodology’s inherent flexibility allows teams to respond to change rather than following a fixed plan. Market conditions, customer preferences, or technology changes can be rapidly incorporated into project planning. This adaptability minimizes risks associated with unforeseen changes and ensures the project remains aligned with business objectives and customer needs.
VI. Agile in Practice: Real-World Examples
Successful companies have embraced the Agile framework and methodology to enhance their productivity, improve collaboration, and deliver high-quality products and services.

Find out by accessing here: Agile Success Stories: Learn from the Giants
VII. Conclusion
Agile project management offers a customer-centric and flexible approach that addresses common challenges in traditional project management. Its iterative nature allows for early and frequent delivery of tangible results, reducing rework and enabling faster time-to-market. Agile’s emphasis on collaboration, transparency, and empowering team members enhances efficiency, productivity, and overall project success.
By embracing Agile methodologies, organizations can overcome scope creep, delayed feedback, and limited adaptability, improving project outcomes and customer satisfaction. Agile project management is a robust framework that enables organizations to be more responsive, adaptive, and customer-focused in today’s dynamic business environment.
AgileBox is a Jira app that helps teams plan, collaborate, and track their agile projects. This is a powerful tool that can help teams improve their agile development process, which is developed by DevSamurai team. AgileBox makes the Agile process seamless, simple, fun, colorful, and productive.
This toolbox is for Agile teams to estimate, prioritize the product backlog, conduct retrospectives, daily standup & team health analysis, with three main features: Planning Poker for Jira, Agile Retrospective for Jira, and Daily Standup for Jira.
Try out our app now: Agile Planning Poker, Retrospectives, Daily Standup for Jira













